Insurance in Nigeria: Barriers, Opportunities and the Lagos Case Study
Insurance plays a crucial role in economic stability and financial protection, yet uptake in Nigeria remains significantly low compared to global benchmarks. Despite the industry’s potential, many individuals and businesses continue to operate without adequate coverage, exposing themselves to unnecessary financial risk.
The State of Insurance in Nigeria
Nigeria’s insurance sector is underdeveloped relative to its economy and population size. According to industry reports, less than 3% of Nigerians have any form of insurance coverage, compared to much higher penetration rates in other emerging markets. Factors such as low financial literacy, trust issues and accessibility challenges hinder widespread adoption.
The sector has struggled with slow growth despite regulatory reforms aimed at boosting consumer confidence. Many insurers operate in a market where risk management is not prioritised, leading to inconsistent engagement from individuals and businesses alike. Additionally, traditional beliefs and economic constraints mean that insurance is often seen as an unnecessary expense rather than a financial safety net.
Barriers to Insurance Adoption: Insights from Lagos
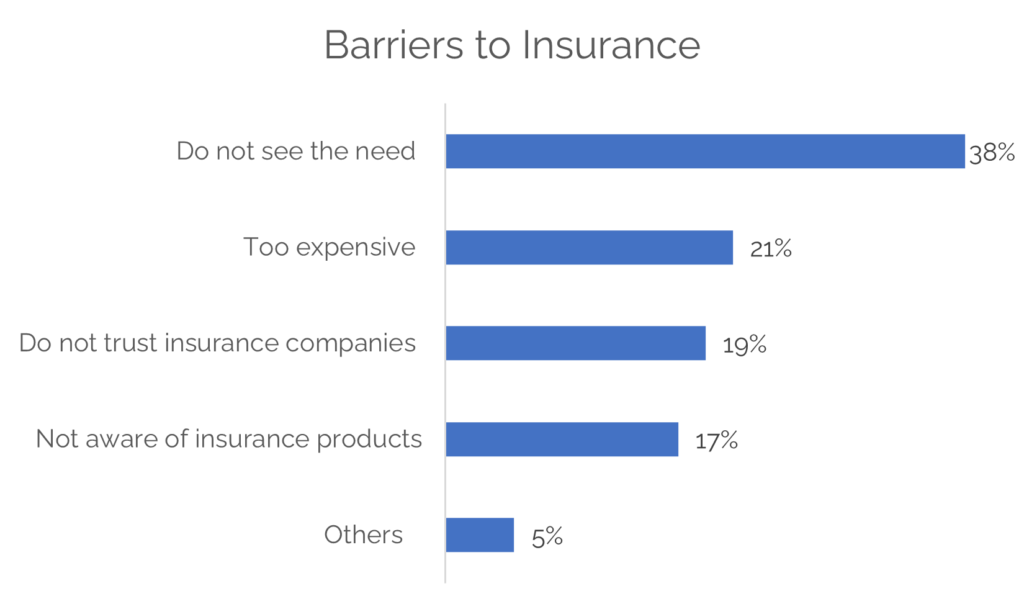
A recent study by VIISAUS examined the barriers to insurance uptake in Lagos, Nigeria’s financial hub. While Lagos is more economically active than many other regions, the challenges affecting insurance adoption remain prevalent. The study identified five key barriers:
- Lack of Perceived Need (38%) – A significant portion of respondents do not see the need for insurance. Many prioritise daily expenses over long-term financial security, believing that insurance is unnecessary unless mandated.
- Cost Perception (21%) – The belief that insurance is too expensive prevents many individuals from considering it. Without flexible payment options, consumers struggle to justify premiums alongside immediate financial responsibilities.
- Trust Issues (19%) – Concerns over claims processing, transparency and reliability discourage many from engaging with insurance providers. The perception that insurers fail to honour claims erodes consumer confidence.
- Lack of Awareness (17%) – Limited understanding of insurance products reduces engagement. Many potential customers do not know what is available or how policies work, making it difficult to make informed decisions.
- Other Factors (5%) – Additional barriers include bureaucratic challenges, accessibility issues and cultural mindsets that limit insurance penetration.
The Way Forward: Strategies for Industry Growth
To bridge the gap between policy offerings and consumer adoption, the Nigerian insurance sector must focus on targeted interventions:
- Consumer Education – Raising awareness and promoting financial literacy can reshape perceptions of insurance as a necessity rather than a luxury.
- Affordable and Flexible Products – Customised plans that cater to different income levels will reduce affordability concerns and improve adoption rates.
- Enhancing Trust and Transparency – Strengthening claims processes, policy clarity and customer service will rebuild confidence in the insurance ecosystem.
- Strategic Engagement – Leveraging digital platforms, partnerships and behavioural insights will enhance accessibility and uptake.
Nigeria’s insurance market holds immense potential, but growth depends on consumer confidence, affordability and education. While Lagos provides valuable insights into these challenges, the findings reflect nationwide trends. Addressing these barriers through industry innovation and policy reforms will be key to increasing adoption and ensuring long-term financial protection for Nigerians.
Sharing is caring!
